Your guide to Vegas HVAC programs, including costs, program length, EPA 608 certification prep, schedule options, and hiring outlook.
Methodology
To compile our list, we took into account accreditation, EPA 608 certification prep, labs and equipment, and schedule flexibility.
Quick Facts for HVAC Training Las Vegas, NV
- Typical program lengths will vary based on several factors, including curriculum and format. Most certificate programs take less than one year to complete, while associate degrees usually take around two years.
- The cost of an HVAC program also spans a wide range, from less than $2,000 to more than $30,000. This will depend on whether you’re pursuing a certificate or associate degree, as well as the length, curriculum, and location of the course.
- You may also have an opportunity to pursue an externship through your program, if they have any partnerships with local companies.
Top Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Programs in Las Vegas (Unranked)
Advanced Training Institute
Advanced Training Institute offers more than just basic training in HVAC/R topics like air conditioning, plumbing, and electrical theory. By the end of class, their graduates will be prepared to test for EPA, HVAC Excellence, 410A, and OSHA certifications to help them launch their new careers.
Credentials: Certificate
Length: 10.5 months
Costs: Contact school to learn more
Lab setup: Contact school to learn more
EPA 608 support: EPA prep included
Externship/placement: Job placement assistance provided
Formats: Daytime and evening courses
National Technical Institute
For aspiring HVAC techs, NTI offers four program options: residential, commercial, HVAC engineer, and automation systems. They’ve also announced the addition of a new commercial refrigeration certification, for current professionals interested in continuing their education.
Credentials: Certificate
Length: three–four months
Costs: $3,255–$7,795
Lab setup: 40–44% of course spent on lab work
EPA 608 support: EPA certification exam included
Externship/placement: Partnerships with local businesses for job placement post-graduation
Formats: Weekday and weekend, morning and evening classes
Quality Technical Training Center
With morning, afternoon, and evening class options, Quality Technical Training Center offers programs spanning 48–192 hours and covering fundamentals of refrigeration, gas heat and brazing, ice machines, and much more.
Credentials: Certificate
Length: 4–16 weeks
Costs: Contact school to learn more
Lab setup: Approximately 16,000 sq ft of classrooms and labs equipped with real working heating, air conditioning, and refrigeration units
EPA 608 support: Offers EPA-approved certification program
Externship/placement: Placement assistance provided through employer partners
Formats: Morning, afternoon, and evening classes
UEI College
UEI’s HVAC program aims to provide students with the knowledge, skills, and hands-on training needed to begin an entry-level technician career, including prep for two certifications: the EPA 608 Certification and the Low GWP Refrigerant Safety Certification.
Credentials: Diploma
Length: 10 months
Costs: $21,500
Lab setup: Lab training with real HVAC equipment included
EPA 608 support: EPA certification prep included in curriculum
Externship/placement: Career support provided, including job placement assistance
Formats: Day and evening classes
Nevada HVAC Technician Requirements
- EPA 608 certification. Under Section 608 of the Clean Air Act, HVAC technicians who are responsible for installing, maintaining, repairing, or disposing of equipment that could release ozone-depleting refrigerants into the atmosphere must obtain an EPA 608 certification.
- State licensing. The state of Nevada does not require a license to practice as an HVAC technician. However, if you plan to open your own business or become a contractor who completes HVAC work, then you must have a Nevada HVAC contractors license issued by the Nevada State Contractors Board (NSCB).
- Licensing Requirements. In order to receive a contractors license, you must submit an application; obtain a Nevada state business license; submit proof of at least four years experience as a journeyman, supervising employee, site foreman, or contractor, or in lieu of work experience proof of a degree or educational training from an accredited degree program; and submit a financial statement prepared by a licensed CPS based on your monetary limit.
How to Choose an HVAC Training Program in Vegas
- Flexible scheduling. While some are able to commit to a full-time program, or even a 2-year associate degree, others may have existing work or family obligations that require a more flexible schedule or prefer a short-term course that will get them in the workforce quicker. When researching schools, think about if you’d rather enroll in a full-time course over a shorter period of time, or a part-time course that spans a longer period.
- Hands-on training. Maintaining control systems is hands-on work, so ensuring that you’ll have access to labs that can help prepare students for their careers is key. Take a look at each school’s syllabus to note how much time you’ll be given to actually work on subjects like electrical troubleshooting, maintaining cooling loads and refrigeration systems in a desert climate, and more.
- Exposure to commercial resorts and casino facilities. Many good schools work to provide real-world experience with actual businesses. Does your school have any partnerships with local companies to provide insights and knowledge, or even externship opportunities? Reach out to each administration office to learn more.
How to Pay for Your HVAC Program
The cost of attending an HVAC school can vary widely, ranging from less than two thousand dollars to more than thirty thousand depending on location, school, certification, and length.1 In addition to this, prospective students should also factor in the costs of tools, exam fees, and licensing. Luckily, most schools also provide multiple payment options to help ease the cost.
- Workforce grants. You may also want to look into government-sponsored programs that provide grants for technical training schools, covering partial or full tuition. Contact your school to learn if they’re eligible for any of these grants.
- Employer sponsorships. Through an employer sponsorship, a company will pay all or part of a student’s tuition, in exchange for that student agreeing to work for them for a certain amount of time after their training. You’ll want to keep in mind that, if you leave employment before the required timeline, you will typically be required to pay back the tuition that the employer covered.
- Private loans. While not all HVAC schools offer federal student loans, they may provide private loan options. It’s important to remember, though, that should you choose this route, you’ll likely end up paying more in interest payments, and your credit score may be affected.
HVAC Career Outlook
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), there remains an outlook of high demand for skilled HVAC technician, as they project an 8% job growth rate through 2034 (“much faster” than the national average across all occupations of 3%).2 They also put the median annual salary at $59,810.3 With its thriving hospitality and commercial industries, concentration of convention facilities, and need for residential services, it’s no wonder that the city is a hub for a rewarding career in HVAC.
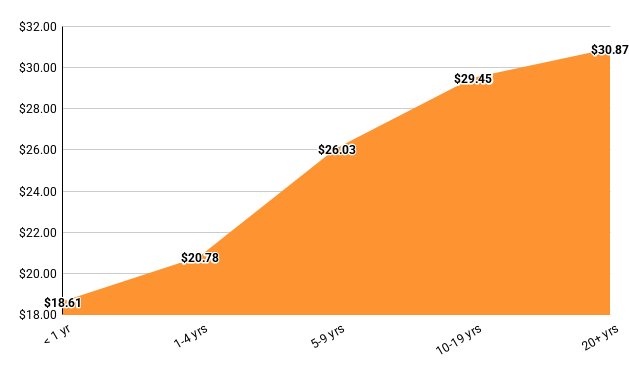
HVAC techs can also look forward to consistent salary growth throughout their careers, from those with less than one year of experience to those with more than 20. Payscale maps out the average salary by experience, with their data showing entry-level salaries at $18.61/hour and late-career salaries at $30.87/hour.4
FAQs
Do I need a state license to start?
Although Nevada does not require HVAC installers, technicians, or mechanics to hold a license, if you plan to start your own business or become a contractor, you must have an HVAC contractors license issued by the NSCB.
Is an EPA 608 certification mandatory?
An EPA 608 certification is required for any professional who handles equipment that could release ozone-depleting refrigerants, as well as most substitute refrigerants, as mandated under Section 608 of the Clean Air Act. Those who do not handle these materials need only receive their license.
How long until I can start work?
Depending on the school, your program can be completed in as little as two weeks or two years. You must then pass any necessary licensing or certification exams. For example, if your work requires you to obtain an EPA certification, you must schedule your exam date at least 72 hours in advance, but can then take the test 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Sources
1https://www.neit.edu/blog/how-much-does-hvac-school-cost
4https://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=HVAC_Technician/Hourly_Rate
